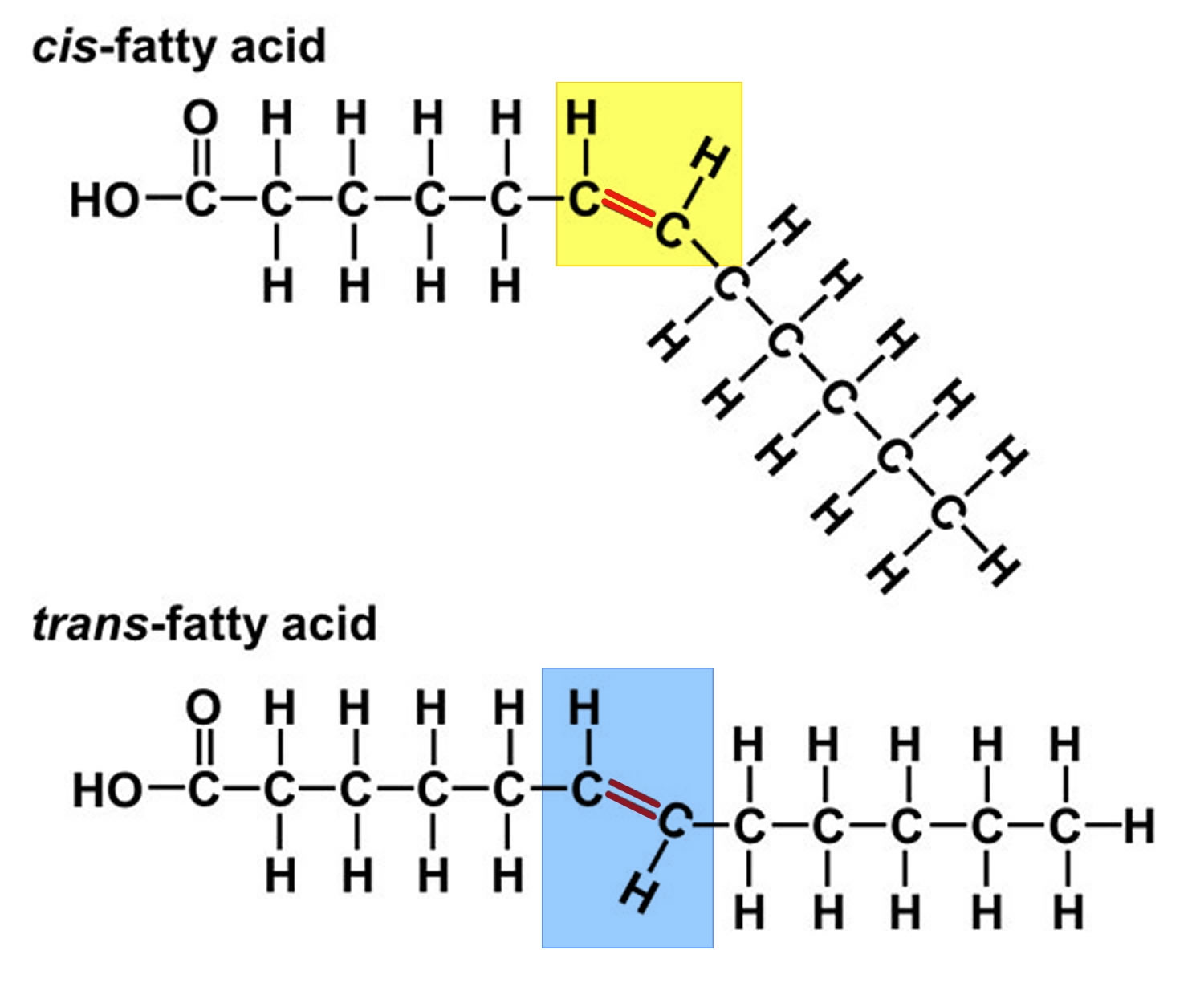
Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure . A triglyceride is a type of lipid (or fat) molecule. Unsaturated fat, a fatty acid in which the hydrocarbon molecules have two carbons that share double or triple bond (s) and are therefore not completely saturated with hydrogen. As a result, close intermolecular interactions. The carbons of the alkene functional group, the site of unsaturation, are in. Fats provide energy, insulation, and storage of fatty acids for many organisms. This molecular structure allows many fatty acid molecules to be rather closely stacked together. Fatty acids are carboxylic acids that are the structural components of many lipids. It is made up of three fatty acid chains. They may be saturated or unsaturated. Most fatty acids are unbranched and contain an even number of. Fats may be saturated (having single bonds) or.
from healthjade.net
They may be saturated or unsaturated. Fats may be saturated (having single bonds) or. It is made up of three fatty acid chains. Fats provide energy, insulation, and storage of fatty acids for many organisms. This molecular structure allows many fatty acid molecules to be rather closely stacked together. A triglyceride is a type of lipid (or fat) molecule. Most fatty acids are unbranched and contain an even number of. As a result, close intermolecular interactions. The carbons of the alkene functional group, the site of unsaturation, are in. Unsaturated fat, a fatty acid in which the hydrocarbon molecules have two carbons that share double or triple bond (s) and are therefore not completely saturated with hydrogen.
Healthy fats
Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure This molecular structure allows many fatty acid molecules to be rather closely stacked together. A triglyceride is a type of lipid (or fat) molecule. This molecular structure allows many fatty acid molecules to be rather closely stacked together. The carbons of the alkene functional group, the site of unsaturation, are in. They may be saturated or unsaturated. Fats may be saturated (having single bonds) or. Most fatty acids are unbranched and contain an even number of. It is made up of three fatty acid chains. Fatty acids are carboxylic acids that are the structural components of many lipids. Fats provide energy, insulation, and storage of fatty acids for many organisms. As a result, close intermolecular interactions. Unsaturated fat, a fatty acid in which the hydrocarbon molecules have two carbons that share double or triple bond (s) and are therefore not completely saturated with hydrogen.
From www.youtube.com
Intro to Saturated Fats, Unsaturated Fats, and Trans Fats YouTube Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure As a result, close intermolecular interactions. A triglyceride is a type of lipid (or fat) molecule. Fats may be saturated (having single bonds) or. It is made up of three fatty acid chains. Unsaturated fat, a fatty acid in which the hydrocarbon molecules have two carbons that share double or triple bond (s) and are therefore not completely saturated with. Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure.
From www.shutterstock.com
Fats Molecule Images Browse 2,942 Stock Photos & Vectors Free Download Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure It is made up of three fatty acid chains. The carbons of the alkene functional group, the site of unsaturation, are in. Fats may be saturated (having single bonds) or. Most fatty acids are unbranched and contain an even number of. A triglyceride is a type of lipid (or fat) molecule. This molecular structure allows many fatty acid molecules to. Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure.
From michaelkummer.com
Polyunsaturated Fats (Not Saturated Fats) Cause Heart Disease Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure Unsaturated fat, a fatty acid in which the hydrocarbon molecules have two carbons that share double or triple bond (s) and are therefore not completely saturated with hydrogen. Fatty acids are carboxylic acids that are the structural components of many lipids. The carbons of the alkene functional group, the site of unsaturation, are in. As a result, close intermolecular interactions.. Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure.
From fity.club
Unsaturated Fat Structure Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure Most fatty acids are unbranched and contain an even number of. They may be saturated or unsaturated. Unsaturated fat, a fatty acid in which the hydrocarbon molecules have two carbons that share double or triple bond (s) and are therefore not completely saturated with hydrogen. A triglyceride is a type of lipid (or fat) molecule. It is made up of. Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure.
From www.dreamstime.com
Structure of Saturated and Unsaturated Fat Stock Illustration Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure As a result, close intermolecular interactions. This molecular structure allows many fatty acid molecules to be rather closely stacked together. Unsaturated fat, a fatty acid in which the hydrocarbon molecules have two carbons that share double or triple bond (s) and are therefore not completely saturated with hydrogen. It is made up of three fatty acid chains. The carbons of. Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure.
From www.alamy.com
3d Illustration of saturated fat Molecule isolated white background Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure The carbons of the alkene functional group, the site of unsaturation, are in. It is made up of three fatty acid chains. They may be saturated or unsaturated. A triglyceride is a type of lipid (or fat) molecule. Fats may be saturated (having single bonds) or. Most fatty acids are unbranched and contain an even number of. Fatty acids are. Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure.
From manualpartkoblenz101.z21.web.core.windows.net
Molecular Diagram Of Saturated Fatty Acid Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure Fats provide energy, insulation, and storage of fatty acids for many organisms. A triglyceride is a type of lipid (or fat) molecule. Fatty acids are carboxylic acids that are the structural components of many lipids. Fats may be saturated (having single bonds) or. Most fatty acids are unbranched and contain an even number of. This molecular structure allows many fatty. Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure.
From openoregon.pressbooks.pub
Fatty Acid Types and Food Sources Nutrition Science and Everyday Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure Fats may be saturated (having single bonds) or. Fatty acids are carboxylic acids that are the structural components of many lipids. Unsaturated fat, a fatty acid in which the hydrocarbon molecules have two carbons that share double or triple bond (s) and are therefore not completely saturated with hydrogen. Fats provide energy, insulation, and storage of fatty acids for many. Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure.
From www.animalia-life.club
Simple Saturated Fat Molecule Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure It is made up of three fatty acid chains. They may be saturated or unsaturated. Unsaturated fat, a fatty acid in which the hydrocarbon molecules have two carbons that share double or triple bond (s) and are therefore not completely saturated with hydrogen. Fats provide energy, insulation, and storage of fatty acids for many organisms. This molecular structure allows many. Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Triglycerides Saturated And Unsaturated Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure They may be saturated or unsaturated. The carbons of the alkene functional group, the site of unsaturation, are in. Fats provide energy, insulation, and storage of fatty acids for many organisms. It is made up of three fatty acid chains. Fatty acids are carboxylic acids that are the structural components of many lipids. A triglyceride is a type of lipid. Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure.
From openoregon.pressbooks.pub
Fatty Acid Types and Food Sources Nutrition Science and Everyday Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure Fatty acids are carboxylic acids that are the structural components of many lipids. This molecular structure allows many fatty acid molecules to be rather closely stacked together. Unsaturated fat, a fatty acid in which the hydrocarbon molecules have two carbons that share double or triple bond (s) and are therefore not completely saturated with hydrogen. It is made up of. Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure.
From nutritionstudies.ucdavis.edu
Nutrition & Health Info Sheets for Health Professionals Fat UC Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure Fats provide energy, insulation, and storage of fatty acids for many organisms. As a result, close intermolecular interactions. It is made up of three fatty acid chains. Most fatty acids are unbranched and contain an even number of. They may be saturated or unsaturated. Fatty acids are carboxylic acids that are the structural components of many lipids. Unsaturated fat, a. Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure.
From bio1151.nicerweb.net
fatunsaturated.html 05_12bSaturatedUnsatFatL.jpg Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure This molecular structure allows many fatty acid molecules to be rather closely stacked together. They may be saturated or unsaturated. Fats provide energy, insulation, and storage of fatty acids for many organisms. A triglyceride is a type of lipid (or fat) molecule. As a result, close intermolecular interactions. Fats may be saturated (having single bonds) or. The carbons of the. Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure.
From getrevising.co.uk
Fat AS1 N&FS Revision Cards in A Level and IB Home Economics Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure Fatty acids are carboxylic acids that are the structural components of many lipids. The carbons of the alkene functional group, the site of unsaturation, are in. Fats may be saturated (having single bonds) or. Most fatty acids are unbranched and contain an even number of. Unsaturated fat, a fatty acid in which the hydrocarbon molecules have two carbons that share. Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure.
From pinterest.com
Molecular structure of different fatty acids / Trans fat can be a Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure A triglyceride is a type of lipid (or fat) molecule. Fats may be saturated (having single bonds) or. It is made up of three fatty acid chains. As a result, close intermolecular interactions. Fats provide energy, insulation, and storage of fatty acids for many organisms. They may be saturated or unsaturated. Unsaturated fat, a fatty acid in which the hydrocarbon. Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure.
From fity.club
Unsaturated Fat Structure Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure Fatty acids are carboxylic acids that are the structural components of many lipids. Fats may be saturated (having single bonds) or. They may be saturated or unsaturated. A triglyceride is a type of lipid (or fat) molecule. The carbons of the alkene functional group, the site of unsaturation, are in. As a result, close intermolecular interactions. This molecular structure allows. Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure.
From circuitdiagramtubfuls.z14.web.core.windows.net
Saturated Fat Vs Unsaturated Fat Diagram Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure As a result, close intermolecular interactions. Fatty acids are carboxylic acids that are the structural components of many lipids. Most fatty acids are unbranched and contain an even number of. This molecular structure allows many fatty acid molecules to be rather closely stacked together. Fats may be saturated (having single bonds) or. It is made up of three fatty acid. Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure.
From www.reddit.com
ELI5 the different fat types mono unsaturated; polyunsaturated Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure Fats provide energy, insulation, and storage of fatty acids for many organisms. As a result, close intermolecular interactions. Fatty acids are carboxylic acids that are the structural components of many lipids. It is made up of three fatty acid chains. Unsaturated fat, a fatty acid in which the hydrocarbon molecules have two carbons that share double or triple bond (s). Unsaturated Fat Molecular Structure.